

Credit: Gonzalo Solari/iStock/Getty Images Plus
ECMWF’s participation in the EU’s Horizon 2020 project APPLICATE has led to a concerted effort to examine the challenges that limit the skill of ECMWF forecasts in Arctic regions.
To improve weather forecasts in the Arctic and beyond, advances have been made at ECMWF in the areas of coupled modelling, process-based diagnostics, and the effective use of observations and data assimilation.
APPLICATE was coordinated by Prof. Thomas Jung from the Alfred Wegener Institute in Germany. The four-year project ended in April 2021.
Coupled modelling and process-based diagnostics
In terms of coupled modelling, the APPLICATE focus at ECMWF was on the representation of snow and the coupling of the atmosphere, the ocean, snow and sea ice.
One of the main sources of forecast errors over snow-covered surfaces is the use of a bulk snow scheme in the current version of ECMWF’s Integrated Forecasting System (IFS).
Representing the snowpack with a single layer of snow leads to an overestimation of the thermal inertia of the snowpack, particularly for deep snowpacks.
As a result, the snow depth tends to be too large, the near-surface air temperature too high, and its diurnal cycle is underestimated.
To address these errors, a multi-layer snow scheme was further developed and evaluated in APPLICATE using supersite observations and novel process-based diagnostics. This scheme represents the snowpack with up to five layers. It is planned to be implemented in IFS Cycle 48r1 in 2022/23.
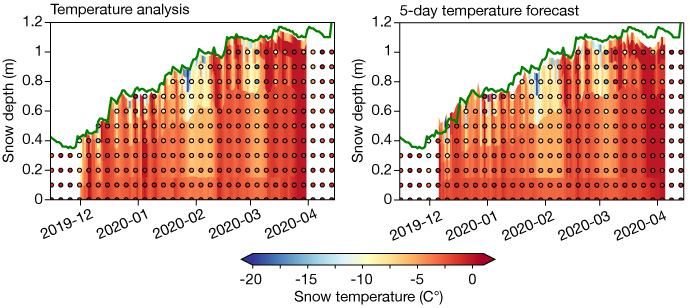
Time–height plots showing the analysis and 5-day forecasts of snow temperature at Sodankylä in Finland with the multi-layer snow model (background colours) and observations (coloured dots) for the 2019/2020 season. The snow depth from observations is superimposed (green line). Observational data are courtesy of Anna Kontu (Finnish Meteorological Institute).
Effective use of observations and data assimilation
APPLICATE demonstrated that all Arctic observing systems have complementary positive impacts on forecast skill, both in the Arctic and in the mid-latitudes.
The impact in the mid-latitudes was shown to be primarily associated with certain flow regimes, like Scandinavian blocking, which favour the propagation of air masses from the Arctic towards the mid-latitudes.
Observing system experiments performed at ECMWF showed that conventional in-situ observations play the most important role during winter.
The same experiments showed that satellite microwave observations play the most important role during summer.
The strong positive impact of microwave observations on predictive skill in summer suggests that improving their use over snow and sea ice, which is currently not optimal, is likely to further improve forecasts in the Arctic and mid-latitudes.
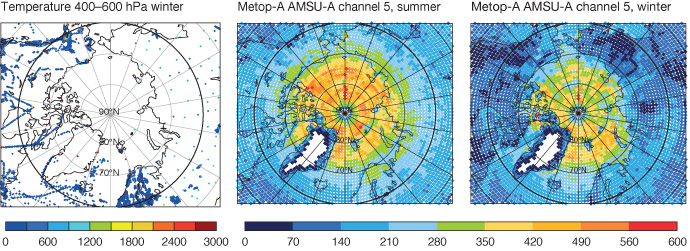
The plots show the number of observations assimilated in the ECMWF operational system from radiosonde and aircraft temperature observations between 400 and 600 hPa for the period December 2017 to March 2018 (left) Metop‐A AMSU‐A channel 5 observations peaking around 650 hPa for June–September 2016 (middle), and the same observations as in the middle plot but for December 2017 to March 2018 (right). Figure from Lawrence et al., 2019, Q J R Meteorol Soc., https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.3628, CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Further reading
For more details, please see the Newsletter article on how APPLICATE contributed to ECMWF’s core activities.
